Atal Innovation Mission (AIM) is the Government of India’s endeavor to promote a culture of innovation and entrepreneurship. Its objective is to serve as a platform for the promotion of world-class Innovation Hubs, Grand Challenges, Start-up businesses, and other self-employment activities, particularly in technology-driven areas.
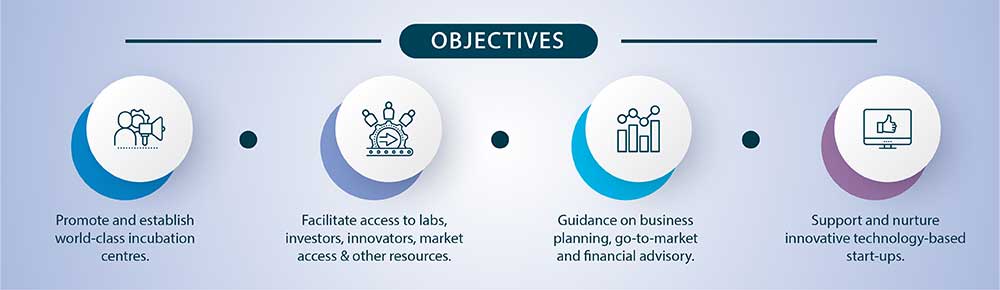
Under its core objectives, AIM intends to support the establishment of new incubation centres called Atal Incubation Centres (AICs) that would nurture innovative start-up businesses in their pursuit to become scalable and sustainable enterprises. Along with AICs, AIM shall also provide scale-up support to a few distinguished incubation centres of the country. These incubation centres, referred to as Established Incubation Centers (EICs) have already been in existence, but AIM intends to further catalyze their performance by providing them scale-up support.
Business incubators are institutions that support entrepreneurs in developing their businesses, especially in the initial stages. These are organizations geared towards speeding up the growth and success of start-ups and early-stage companies. Incubation is usually done by institutions that have experience in the business and technology world.
Incubation support includes providing technological facilities and advice, initial growth funds, network and linkages, co-working spaces, lab facilities, mentoring, and advisory support. They are often a good path to capital from angel investors, government organizations, economic-development coalitions, venture capitalists, and other investors.
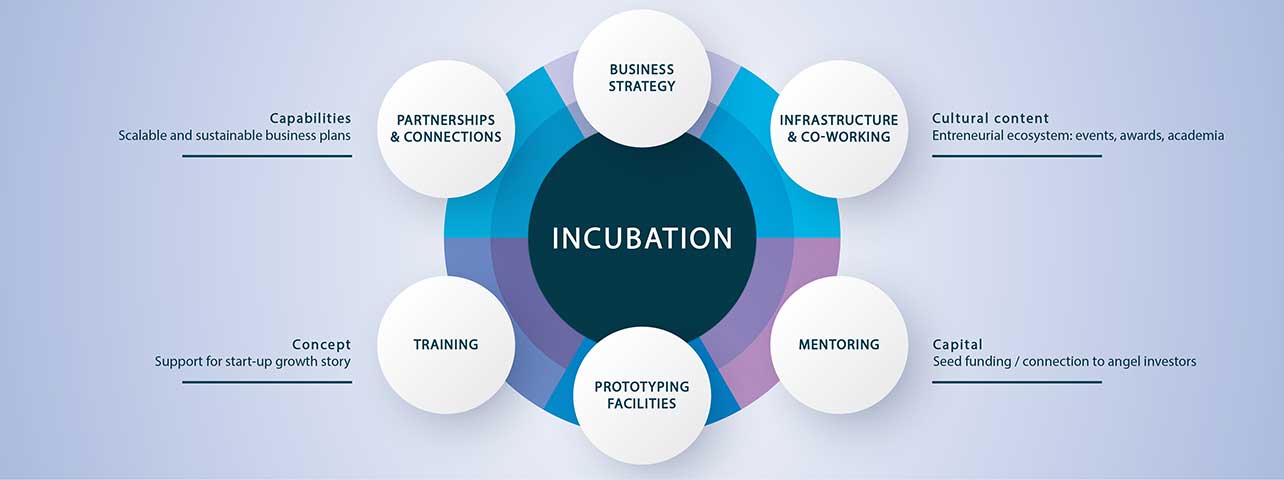
As early-stage hand-holders, incubators act as an integral part of the start-up ecosystem. They act as a catalyst for both regional as well as national economic development. There are different types of incubators: Academic institutions; Non-profit development corporations; For-profit development ventures; Venture capital firms, and combinations of the above. Incubators vary in their strategies. Some are located in an actual physical space meant to foster networking between incubatee entrepreneurs and others in entrepreneurial space. While others operate on a virtual basis. Incubators sometimes call themselves accelerators instead, often when they are geared towards jump-starting businesses that are more developed. Also, business incubators differ from research and technology parks in their dedication towards supporting start-ups and early-stage companies. Research and technology parks tend to be large-scale projects that house organizations ranging from government institutions, corporates, university labs to very small companies. They seldom offer business assistance services, unlike business incubators. Rather, it will be good to say that business assistance services are the hallmark of business incubators.